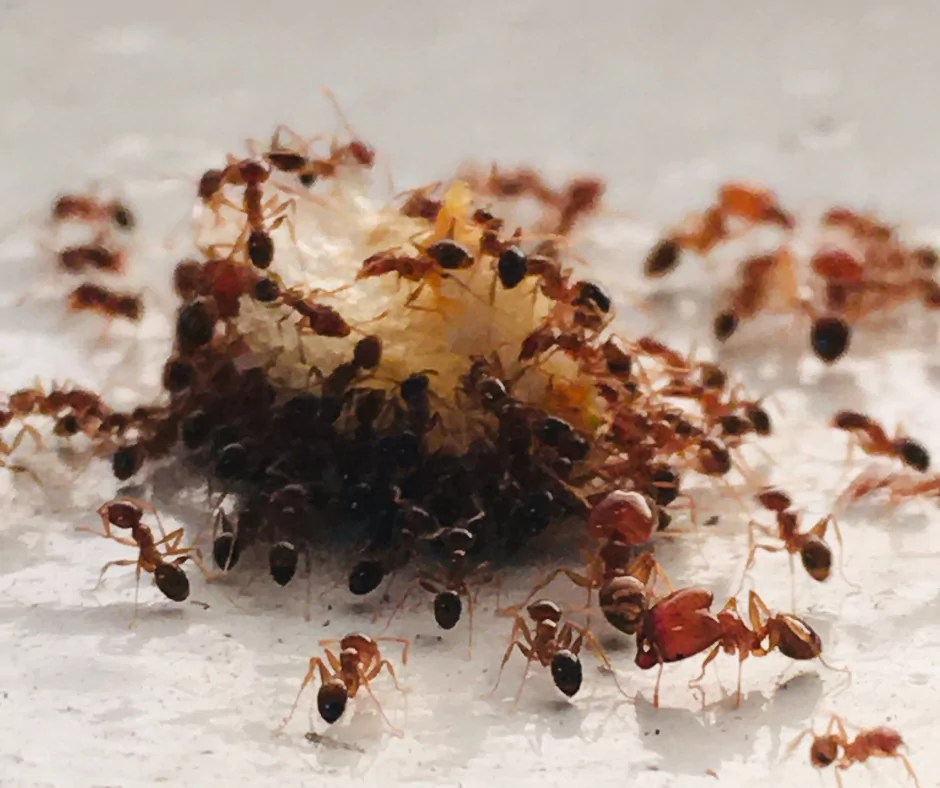
What is insect sociality?
Sociality is how members of the animal kingdom interact with one another and associate in social groups or cooperate with each other. Sociality is important and has become a response to evolutionary pressures in order for insects to survive. Insects are classified by a caste system or a structured hierarchy where some are in the most social subset and some are in the least social subset. There are also subsets of the caste that are partially social or interact in ways that are less social than the members of the most social subset. The range of sociality in insects from most social to least social is eusocial, semisocial, quasisocial, communal or subsocial and solitary.
Why does it matter whether insects are social or not?
Sociality can dictate the behaviors of the insects and how they might interact with people and their environments. Social insects can be more aggressive to people and destructive to infrastructures depending on the species. Some social insects can destroy trees and crops and some can even destroy buildings if they are not properly handled. Solitary insects tend to be less aggressive and are less likely to cause harm to humans. Solitary insects also tend to be less likely to cause structural damage. Social insects are ecologically important because some insects are known as ecosystem engineers. Ecosystem engineers are organisms that work to create, change or impact a habitat whether it is positively or negatively. Some positive effects they have on the ecosystems include the production of food and other useful materials, seed dispersal, breakdown of waste and pest control for some other types of insects. Some ants for example can positively influence the ecosystem by keeping the soil and surrounding areas clean.
Bees, specifically honey bees also positively influence the environment by pollinating crops. There are also negative effects associated with ecosystem engineers including the harming of plants, wooden structures and homes and generally being an invasive nuisance to people and potentially stinging or biting. Leaf-cutter ants for example are social insects that harm plants by collecting pieces of leaves to grow the fungus that they feed off of. Carpenter ants also negatively impact the ecosystem by damaging wooden structures. While some ecosystem engineers possess more negative attributes, there are many that influence the ecosystem in positive ways and their population may be protected to ensure they are well maintained. The insects that cause harm and structural damage are the ones that may need to be evaluated by pest control and removed.
What is a social insect?
Social insects exhibit four social behaviors or traits that include sharing a common nest site, cooperating in care for the young, working to benefit the few that reproduce and offspring working while their parents are still alive (generational overlap). Social insects work as a team and cooperate with one another to accomplish a common goal. Only about two percent of insects are truly social (eusocial) or exhibit all of the behaviors of a social insect. Almost all ants of various types tend to be eusocial and possess all of the social traits. Eusociality has evolved from its primitive form to a more advanced form. The evolution of sociality is based on four main factors, ecological contributions, kin selection, delayed benefits and multi-level selection. There are many advantages to eusociality for insects and by adapting to certain changes, insects have been able to increase their chance for survival and reduce their amount of fatalities. Once an insect has made the transition from the primitive eusociality to the more advanced form of eusociality, it is known as the point of no return, because insects cannot revert back to being solitary. They will then be a eusocial insect from that point forward due to the evolutionary standards.
What are semisocial and quasisocial insects?
Semisocial insects share a common nest with their species, care for offspring and have a worker caste system in which members of the nest provide for the queen or the ones that produce offspring. Quasisocial insects share a common nest and care for each other’s offspring but do not have a worker caste system. An example of a semisocial insect is a halictid bee and an example of a quasisocial insect is a euglossine bee.
What are presocial insects?
Species of insects that lack one or more of the social insect traits is referred as presocial insects. Furthermore, presocial insects are classified as either subsocial or parasocial insects. Subsocial insects provide parental care for their offspring and parasocial insects have a common nest site but lack one or more of the other social behaviors or traits of social insects. Communal insects also fit into the category of presocial insects because they live together but do not meet any of the other traits of a social insect. An example of a subsocial insect is a cockroach and an example of a communal insect is a digger bee.
What is a solitary insect?
A solitary insect is an insect that doesn’t possess any of the four characteristics of a social insect. Solitary insects live by themselves and don’t interact with other insects. They reproduce but will not care for their offspring or for the offspring of others within their species. They build their nests, and work and live independently. Most insects are solitary but an example of a specific solitary insect is a mud dauber wasp.
What can be done about harmful and damaging social insects?
When social insects start being a problem for the human environment, they need to be managed. For example if there is a termite infestation in someone’s home, that needs to be taken care of to ensure nothing results in permanent or lasting damage, causing need for extensive repairs and excessive costs. If you have a nest or hive of stinging insects, they will need to be removed to ensure no one on the property is harmed. Summit Wildlife Removal has skilled pest control technicians who can properly identify the species of insects and offer pest control and pest maintenance to remove them from your property and ensure they do not return. For a free estimate and to schedule your removal contact us today.